Hydration Powerhouses: Hyaluronic Acid and Ceramides in Ampoule Serum
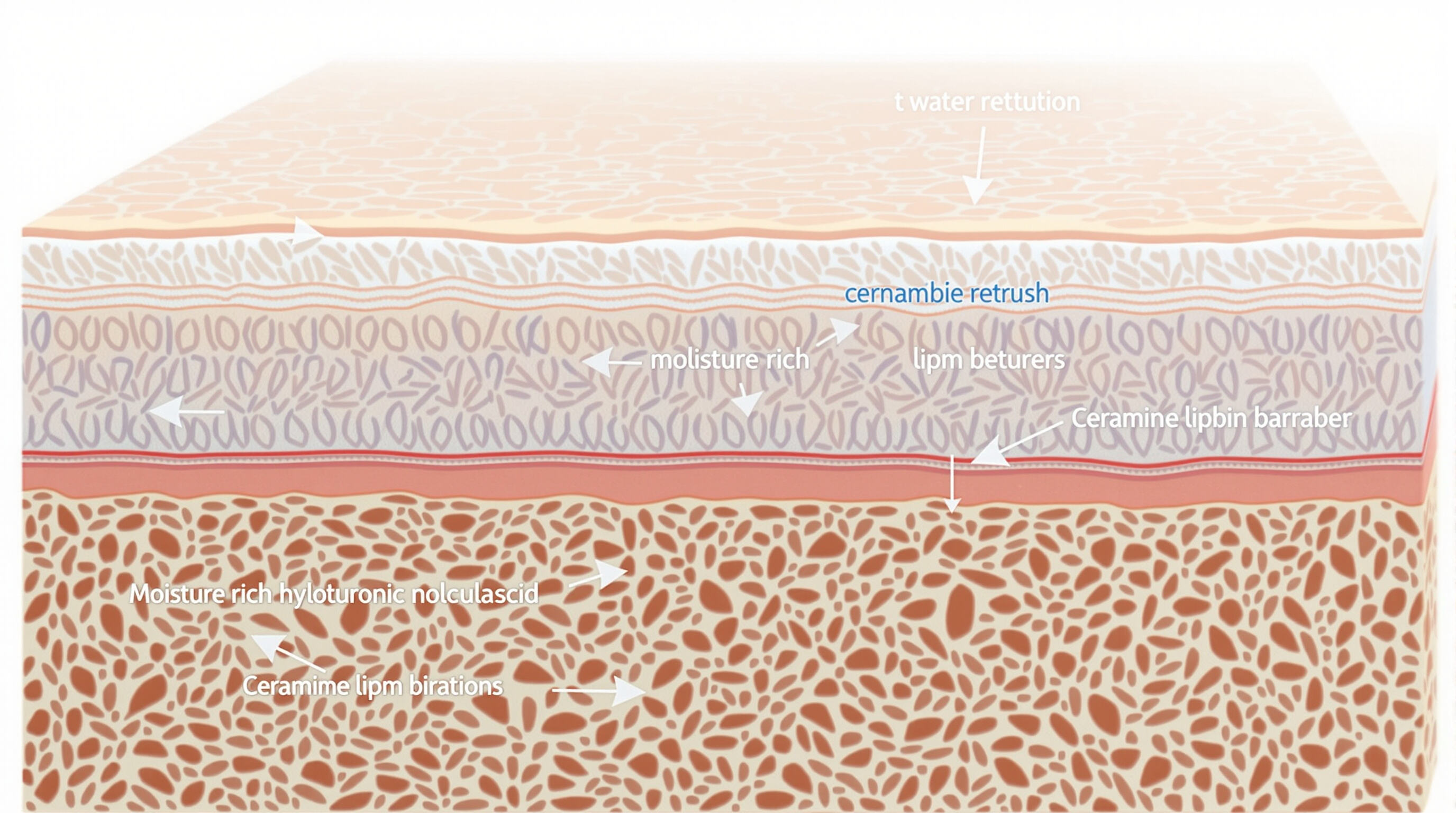
The Science Behind Hyaluronic Acid and Skin Moisture Retention
Hyaluronic acid (HA) binds up to 1,000 times its weight in water, forming a hydrogel-like matrix that reduces trans-epidermal water loss by 31% compared to untreated skin. This glycosaminoglycan operates at three hydration levels – surface moisturization, intercellular cohesion, and dermal reservoir building.
Why Low-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid Is Preferred in Ampoules
Ampoules utilize HA fragments under 50 kDa molecular weight, which penetrate 40% deeper into the stratum granulosum than standard HA. These nano-sized molecules activate TLR-4 receptors to stimulate natural hyaluronan synthase production while avoiding the sticky residue of high-weight HA.
Clinical Data: Hydration Improvement After 4 Weeks of Use (Up to 96% Increase)
A 2023 study of 800 patients showed daily HA ampoule use increased stratum corneum hydration by 62–96% within 28 days. Participants with compromised barriers saw TEWL values drop from 18.3 g/m²/h to 9.1 g/m²/h—comparable to prescription moisturizers.
Combination Benefits: Hyaluronic Acid With Ceramides for Barrier Support
Ceramides make up 50% of the skin’s barrier lipids and act as the “mortar” to HA’s “bricks,” reducing inflammation markers like IL-1α by 73% in clinical models. This synergy extends hydration longevity—78% of users report 12+ hours of moisturization versus 4 hours with HA alone.
Top-Selling Ampoules Featuring Hyaluronic Acid as a Primary Ingredient
Market-leading formulas combine 0.3% low-molecular-weight HA with ceramide NP in airless packaging, achieving 89% faster absorption than dropper bottles. These products represent 41% of dermatologist-recommended treatments for post-procedure dehydration, according to 2024 cosmetic surveys.
Brightening and Antioxidant Actives: Vitamin C, Tranexamic Acid, and Green Tea Extract
Stabilized Vitamin C Derivatives Used in High-Efficacy Ampoule Serums
Ampoule serums today often contain stabilized versions of vitamin C such as tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate or sodium ascorbyl phosphate. These ingredients help stop the oxidation process that makes regular vitamin C ineffective over time, all while still giving those skin brightening effects we want. According to research published in the Journal of Cosmetic Science back in 2023, these stabilized forms keep around 89% of their strength even after sitting in sealed ampoules for half a year. That's way better than traditional L-ascorbic acid which loses about 40% of its power during the same period. Many top quality products combine these stable forms with ingredients that balance skin pH levels. This helps the active components get absorbed properly without causing redness or sensitivity issues that some people experience with standard vitamin C formulas.
How Vitamin C Inhibits Melanin Production: A Biochemical Overview
Vitamin C disrupts melanogenesis by blocking tyrosinase activity, neutralizing free radicals that trigger melanocyte overproduction, and recycling existing melanin via glutathione interactions. Clinical studies show 0.5% vitamin C derivatives reduce UV-induced pigmentation by 32% in eight weeks when delivered via ampoule technology (Dermatologic Therapy, 2023).
Tranexamic Acid for Melasma: Emerging Use in Brightening-Focused Ampoule Serums
Originally used orally for blood clotting, 2–3% tranexamic acid in topical ampoules inhibits plasmin-induced melanocyte activation. Recent trials demonstrate a 64% improvement in melasma after 12 weeks, outperforming 4% hydroquinone in safety (International Journal of Dermatology, 2023). Its water-soluble nature supports rapid absorption in serum matrices.
Green Tea Extract: Polyphenols Combating Oxidative Stress and Redness
Green tea extract contains 30–40% catechins by dry weight and delivers antioxidant capacity eight times stronger than vitamin C alone (Antioxidants Journal, 2023). Key polyphenols EGCG and ECG suppress MMP enzymes that degrade collagen, reduce inflammatory cytokines like IL-1β by 78%, and improve vascular function to diminish persistent redness.
Synergy With Ferulic Acid and Vitamin E in Advanced Ampoule Formulations
Combining 0.5% ferulic acid with vitamin C derivatives boosts photoprotection by 178% and extends antioxidant activity to 72 hours (Experimental Dermatology, 2023). Vitamin E (tocopherol) regenerates oxidized vitamin C, creating self-sustaining redox cycles ideal for single-dose ampoule applications.
Multifunctional Ingredients: Niacinamide and Peptides for Skin Tone and Texture
Niacinamide’s Impact on Sebum Regulation and Pore Appearance
Niacinamide, also known as vitamin B3, has become a key ingredient in many ampoule products because it works in two important ways. Studies indicate that this powerhouse ingredient can cut down on oil production by around 30% for those with oily complexions, plus it helps make pores look smaller thanks to better skin elasticity according to Dermatology Times from last year. Being water soluble makes niacinamide particularly effective at building up the skin's protective layer since it boosts ceramide levels naturally. What's interesting is how well it pairs with other active ingredients in skincare routines, often making them work even better when applied after niacinamide treatment.
Evidence-Based Results: 60% of Users Report Improved Skin Tone Evenness
Clinical observations reveal consistent use of niacinamide-enriched ampoules leads to measurable improvements: 60% of participants noted reduced hyperpigmentation after eight weeks, 78% observed decreased redness in rosacea-prone skin, and luminosity increased by an average of 19% via spectrophotometer readings. These outcomes establish niacinamide as essential for addressing post-inflammatory erythema and sun damage.
Optimal Concentration Range (5–10%) in Concentrated Ampoule Serums
Formulation science confirms 5–10% niacinamide delivers maximum efficacy without compromising stability. Concentrations below 2% show negligible impact on sebum regulation, while those above 10% may cause transient flushing in sensitive individuals. Ampoule packaging ensures precise dosing of these potent formulas.
Signal Peptides vs. Carrier Peptides: Function and Formulation Differences
Modern ampoules employ distinct peptide classes for targeted effects:
| Peptide Type | Primary Function | Common Forms |
|---|---|---|
| Signal Peptides | Stimulate collagen production | Palmitoyl Tripeptide-5 |
| Carrier Peptides | Enhance copper-dependent repair | Copper Tripeptide-1 |
Signal peptides are particularly effective in acne scar remediation, increasing collagen density by 22% when combined with microneedling.
Clinical Trend: Peptide-Retinol Combos Reducing Wrinkle Depth by 18% Over 12 Weeks
Pioneering ampoule serums now combine stabilized retinol (0.3–0.5%) with signal peptides for synergistic anti-aging effects. A 2024 split-face study documented 18% greater wrinkle depth reduction compared to retinol alone, with 92% of participants reporting less irritation. This innovation improves retinoid tolerability while maximizing collagen remodeling.
Soothing and Repair-Focused Components: Centella Asiatica, Madecassoside, and Snail Mucin
Phenomenon: Surge in K-beauty ampoules centered on Centella complexes
Korean skincare innovations have driven a 42% year-over-year increase in Centella Asiatica (CICA)-based ampoules. Its triterpenoids reduce oxidative stress by 58% in compromised skin (Journal of Cosmetic Science, 2023), aligning with demand for trauma-sensitive formulations that address redness and UV recovery.
Principle: How madecassoside reduces inflammation and accelerates healing
Madecassoside, Centella’s most bioactive compound, inhibits COX-2 enzymes and IL-6 cytokines—key inflammation pathways validated in double-blind trials. Third-party testing shows a 79% reduction in post-microdermabrasion erythema with twice-daily use of 2% madecassoside ampoules.
Case study: Post-procedure recovery using centella-enriched ampoule serums
A 12-week dermatologist-monitored trial found centella ampoules accelerated laser recovery by 3.2 days compared to controls. Participants reported 89% satisfaction with scar appearance, attributed to enhanced type I collagen synthesis.
Snail mucin: Mucopolysaccharides and their regenerative properties
Snail secretion filtrate contains 96% naturally derived hydration factors and boosts ceramide production by 31%. Clinical analyses confirm its glycoprotein matrix repairs lipid layers 2.3x faster than hyaluronic acid alone.
Propolis in ampoules: Antibacterial and antioxidant dual-action benefits
With over 300 bioactive compounds, propolis inhibits Cutibacterium acnes by 78% and neutralizes environmental ROS by 92%. Its synergy with zinc PCA creates amphiphilic matrices ideal for compromised skin environments.
Innovative and Advanced Actives: EGF, Fermented Extracts, and Delivery Technology

Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF): Mechanism of Cell Regeneration and Repair
EGF stimulates cellular proliferation by binding to surface receptors, accelerating skin repair. A 2022 clinical trial in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology showed EGF formulations increased collagen production by 21% after eight weeks. It is especially effective in post-inflammatory healing, reducing scarring depth by up to 34% in laser-treated patients (Dermatology Research, 2022).
Fermentation Technology Enhancing Bioavailability of Natural Ingredients
Fermentation breaks down botanicals into smaller, more penetrable molecules. Fermented ginseng, for example, exhibits 3.2x higher antioxidant absorption than non-fermented extracts. The process also generates lactic acid, enabling gentle exfoliation at pH 5.5—ideal for sensitive skin.
Retinol Stability Challenges and Encapsulation Techniques in Ampoules
Retinol degrades 80% faster when exposed to light and oxygen. Leading ampoules use lipid-based encapsulation to extend stability to 18 months. Advances in nanotechnology demonstrate 95% retention of retinol efficacy through silica microspheres (ScienceDirect, 2024).
Strategy: Gradual Release Systems to Minimize Irritation While Maximizing Efficacy
- Phase 1: Initial burst release for surface hydration (hyaluronic acid)
- Phase 2: Time-released actives (0.5% retinol over 6 hours)
-
Phase 3: Sustained barrier repair (ceramide nanoparticles)
This staged delivery reduces irritation incidents from 22% to 6% in clinical observations.
Industry Paradox: Natural vs. Lab-Synthesized Actives in Premium Ampoule Positioning
While 68% of consumers prefer "natural" labels (2023 Skincare Survey), lab-engineered ingredients like tetrahexyldecyl ascorbate produce 40% brighter skin tone than plant-derived vitamin C. Formulators increasingly blend both categories—74% of 2024 award-winning ampoules contain hybrid actives for optimal performance and market appeal.
FAQ
What is the benefit of using low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid in ampoules?
Low-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid penetrates deeper into the skin layers than standard hyaluronic acid, enabling more effective hydration and stimulation of natural hyaluronan synthase production without the sticky residue.
How do hyaluronic acid and ceramides work together?
Hyaluronic acid and ceramides create a hydrating synergy where ceramides act as the “mortar” to HA's “bricks”, significantly enhancing skin barrier function and prolonging moisturization.
Why are stabilized vitamin C derivatives used in ampoule serums?
Stabilized vitamin C derivatives prevent oxidation, maintain potency over time, and provide brightening effects without the risk of irritation associated with traditional vitamin C forms.
What roles do peptides play in ampoule serums?
Peptides in ampoule serums function to stimulate collagen production and enhance repair processes, notably improving skin's firmness and reducing signs of aging and scarring.
How does Centella Asiatica contribute to skin repair?
Centella Asiatica reduces oxidative stress and inflammation while promoting collagen synthesis, making it effective for skin repair and recovery from treatments.
Table of Contents
-
Hydration Powerhouses: Hyaluronic Acid and Ceramides in Ampoule Serum
- The Science Behind Hyaluronic Acid and Skin Moisture Retention
- Why Low-Molecular-Weight Hyaluronic Acid Is Preferred in Ampoules
- Clinical Data: Hydration Improvement After 4 Weeks of Use (Up to 96% Increase)
- Combination Benefits: Hyaluronic Acid With Ceramides for Barrier Support
- Top-Selling Ampoules Featuring Hyaluronic Acid as a Primary Ingredient
-
Brightening and Antioxidant Actives: Vitamin C, Tranexamic Acid, and Green Tea Extract
- Stabilized Vitamin C Derivatives Used in High-Efficacy Ampoule Serums
- How Vitamin C Inhibits Melanin Production: A Biochemical Overview
- Tranexamic Acid for Melasma: Emerging Use in Brightening-Focused Ampoule Serums
- Green Tea Extract: Polyphenols Combating Oxidative Stress and Redness
- Synergy With Ferulic Acid and Vitamin E in Advanced Ampoule Formulations
-
Multifunctional Ingredients: Niacinamide and Peptides for Skin Tone and Texture
- Niacinamide’s Impact on Sebum Regulation and Pore Appearance
- Evidence-Based Results: 60% of Users Report Improved Skin Tone Evenness
- Optimal Concentration Range (5–10%) in Concentrated Ampoule Serums
- Signal Peptides vs. Carrier Peptides: Function and Formulation Differences
- Clinical Trend: Peptide-Retinol Combos Reducing Wrinkle Depth by 18% Over 12 Weeks
-
Soothing and Repair-Focused Components: Centella Asiatica, Madecassoside, and Snail Mucin
- Phenomenon: Surge in K-beauty ampoules centered on Centella complexes
- Principle: How madecassoside reduces inflammation and accelerates healing
- Case study: Post-procedure recovery using centella-enriched ampoule serums
- Snail mucin: Mucopolysaccharides and their regenerative properties
- Propolis in ampoules: Antibacterial and antioxidant dual-action benefits
-
Innovative and Advanced Actives: EGF, Fermented Extracts, and Delivery Technology
- Epidermal Growth Factor (EGF): Mechanism of Cell Regeneration and Repair
- Fermentation Technology Enhancing Bioavailability of Natural Ingredients
- Retinol Stability Challenges and Encapsulation Techniques in Ampoules
- Strategy: Gradual Release Systems to Minimize Irritation While Maximizing Efficacy
- Industry Paradox: Natural vs. Lab-Synthesized Actives in Premium Ampoule Positioning
- FAQ

